Having previously built a startup and worked as a project manager at another company, I have seen firsthand how software development cycles can extend over months or even longer. Recently, however, advancements in AI-assisted coding—ranging from AI-integrated IDEs to large language model (LLM) development tools—have significantly changed the landscape. Tasks that once required extensive time and effort can now be completed within days, reshaping the traditional Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) approach.
To appreciate the scale of this transformation, consider the traditional development timelines: industry research shows that (as of 2023) 61.6% of software development companies typically deliver custom software in 4-6 months, with the average delivery time being 4.5 months. Only 7.7% of developers can deliver basic software in less than 2 months. These extended timelines translate directly to costs, with the average custom software project priced around $36,000, and 61.6% of companies charging between $20,000-$40,000 for general utility software.
Drawing from my personal experiences as well as recent industry insights, this article explores how AI-driven coding automation impacts SaaS adoption in both the short and long term, discusses differing viewpoints on this shift, identifies industries that may face disruption or remain resilient, and offers practical strategies for SaaS providers adapting to these changes.
Key Takeaways
- AI-assisted coding is dramatically shortening development cycles from months to days
- Organizations are shifting budgets from traditional SaaS to custom AI-powered solutions
- SaaS providers must evolve toward "SaaS 3.0" with AI integration, composability, and value-based pricing
- Complex enterprise applications and highly regulated industries will resist disruption longer
- The future likely holds a hybrid approach combining AI-powered customization with SaaS reliability
Short-Term Impacts of AI-Assisted Coding on SaaS
Shifting SaaS Budgets and Adoption Strategies
Organizations are currently reassessing IT spending, shifting budgets previously dedicated to packaged SaaS subscriptions toward AI-powered internal projects. CIOs increasingly believe custom-built AI solutions offer greater flexibility and value compared to single-purpose SaaS applications. For example, enterprise leaders are beginning to divert investments from traditional SaaS to generative AI initiatives.
Companies are already developing internal tools—such as customized CRM systems—using generative AI, thereby reducing their dependence on external SaaS providers. Even Salesforce has acknowledged potential shifts in client investment toward generative AI projects, a trend that has impacted its market perception and stock value.
Emerging Signs of Disruption
Certain industries—including finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing—are already experiencing noticeable disruption from AI-powered software development. Companies like Klarna and IBM exemplify this trend by replacing various SaaS tools with AI-based solutions, reducing roles previously filled by human employees.
CRM solutions, traditionally reliant on subscription models, are particularly vulnerable as AI enables businesses to rapidly develop tailored CRM functionalities. Additionally, common workflows, such as employee onboarding, are increasingly managed through custom-built, AI-assisted apps—further diminishing traditional SaaS market share.
Evolution of Pricing Models
The rise of AI-assisted development is prompting SaaS companies to revisit their pricing strategies. High operational costs for generative AI services have driven the adoption of innovative models, including usage-based or "success-based" pricing. For example, Intercom's AI chatbot "Fin" now charges clients only when a query is successfully resolved, marking a notable shift from conventional per-seat pricing structures.
Meanwhile, traditional SaaS providers experimenting with premium AI add-ons risk pushing customers toward developing their own in-house solutions.
Long-Term Outlook: Transformation or Obsolescence?
"Do-It-Yourself" vs. SaaS 3.0
Opinions differ regarding the long-term impact of AI on SaaS. Some predict a shift toward a more "do-it-yourself" environment, where businesses opt to build custom software in-house thanks to the accessibility and affordability of AI tools. Others envision an evolved SaaS model—"SaaS 3.0"—in which providers deeply integrate AI to offer both the stability of managed services and extensive customization.
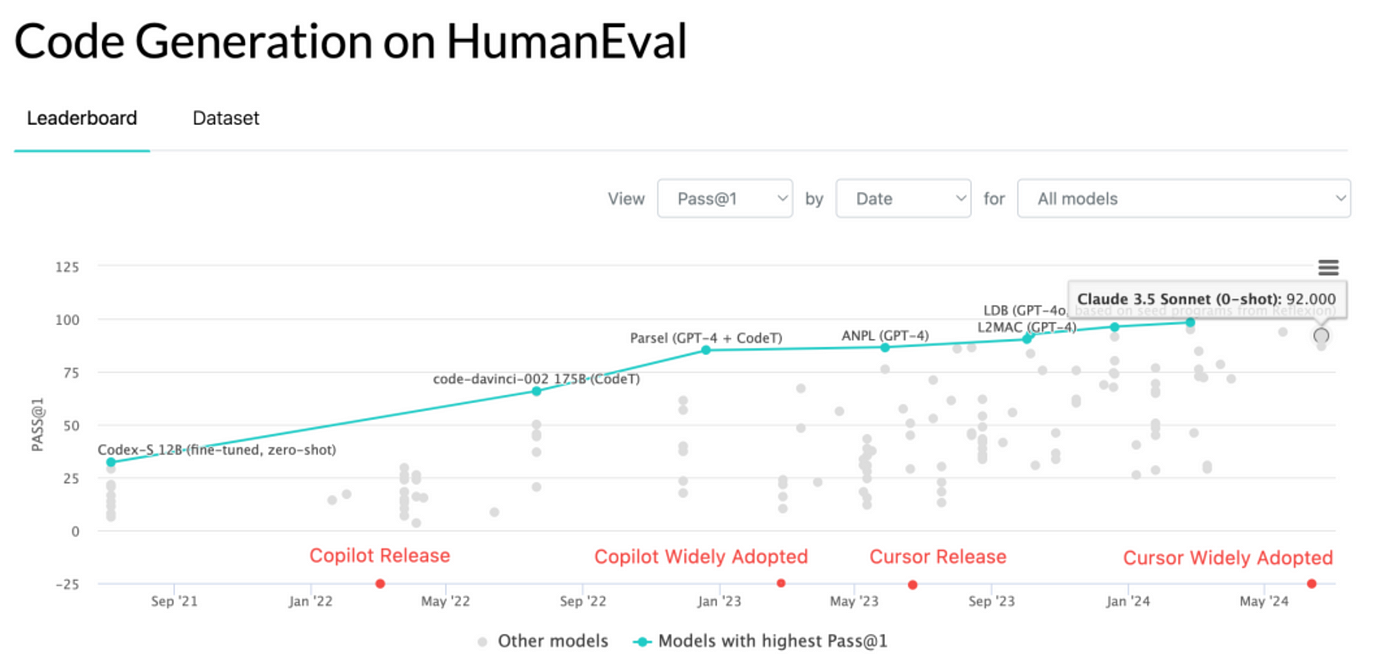
The rapid evolution of AI coding capabilities as measured by the HumanEval benchmark.
The graph above shows how Pass@1 scores (percentage of coding problems solved correctly on first attempt) have improved dramatically from early models like Codex (32%) to Claude 3.5 Sonnet (92%). This exponential improvement in AI coding performance over just three years directly correlates with the shortened development cycles discussed in this article. Note how the releases of AI-powered tools like GitHub Copilot and Cursor IDE have coincided with significant leaps in code generation capabilities.
Personal Reflection on AI's Impact
Reflecting on my experiences, I recall the extensive prototyping and iterative development that went into launching my startup, Klank. What once took many months of work can now be accomplished in a fraction of the time with AI tools. Similarly, while I could always build a website from scratch, doing so without a previous template used to require a significant time investment—something I had little free of at the time. The only alternative was to use a SaaS website builder like Squarespace or Wix. But now, even amidst my law studies and other commitments, I can now create a fully customized website—such as the one you're reading this on—in just a day or two. These personal milestones highlight how AI has not only accelerated software development but also reshaped the value proposition of SaaS.
Analyzing Industry Vulnerability and Resilience
Industries Facing Immediate AI Disruption
- Website Builders and Basic Applications: AI-driven website creation services, like Wix's AI builder, can rapidly produce customized websites, reducing the need for traditional subscription-based tools.
- Workflow Automation and Low-Code Platforms: Tools such as Zapier and Microsoft PowerApps face increased competition as AI-generated scripts become more accessible, challenging the need for specialized SaaS tools.
- Single-Function SaaS Tools: Simple utilities—including file conversion, task management, and basic analytics apps—may become less attractive as custom app development becomes more streamlined with AI.
Industries Likely to Withstand AI Disruption
- Complex Enterprise Solutions: ERP systems and complex CRM solutions that require significant customization, integration, and compliance management remain difficult to replicate quickly.
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure: Given the critical nature of cybersecurity, specialized SaaS solutions with robust security measures will continue to be essential.
- Highly Regulated Sectors: Industries such as healthcare, finance, and legal rely on established SaaS providers to ensure compliance and security, making them less susceptible to disruption.
Strategic Adaptations for SaaS Providers
As AI reshapes software development, SaaS providers must evolve their strategies to remain competitive. The following adaptations represent key opportunities for SaaS businesses to thrive in this changing landscape:
Direct AI Integration
Integrating AI capabilities into existing SaaS products can significantly enhance their value. For example, Microsoft's Copilot in Office 365 and Adobe's AI tools in Creative Cloud have transformed their platforms, streamlining workflows and automating routine tasks.
Customization and Composability
Offering more APIs, plugins, and low-code tools enables SaaS companies to provide flexible, customizable solutions that cater to specific customer needs. This transforms SaaS from a fixed product into a dynamic service that can evolve with the user.
Value-Based Pricing Models
Flexible, outcome-based pricing models that align costs with actual user value are emerging. Intercom's AI chatbot "Fin"—which charges only when a query is successfully resolved—is a prime example of this approach.
Emphasis on Security and Trust
Highlighting robust security measures, compliance standards, and dedicated customer support helps maintain user trust in SaaS solutions, even as DIY alternatives become more attractive.
Establishing AI Partnerships
Collaborating with leading AI technology providers allows SaaS companies to rapidly integrate advanced AI features into their products, ensuring they stay competitive without the need for extensive in-house development.
Hybrid and Service-Oriented Offerings
Developing hybrid solutions that combine customizable AI capabilities with reliable SaaS infrastructure and support can enhance customer satisfaction, blending the best of both worlds.
"...Agents will come together to change every SaaS application category, and building custom applications will be driven by software (i.e. 'service as software')."
— Satya Nadella, Microsoft CEO
Conclusion
AI-driven coding automation is reshaping the software development landscape. In the short term, businesses are rethinking their SaaS adoption strategies by shifting budgets toward in-house, AI-powered projects. In the long term, while some predict a "do-it-yourself" future that could bypass traditional SaaS, the prevailing view is that SaaS will evolve—integrating AI to become more adaptive, intelligent, and customizable (often referred to as "SaaS 3.0").
"SaaS isn't dying—it's evolving. The most successful SaaS companies will position their core products as platforms that AI agents seamlessly integrate with and enhance, not replace."
— Ahrvo Labs
My personal experience reflects this evolution: what once required extensive effort and long development cycles can now be accomplished in days with AI assistance. This rapid transformation underscores that while complex enterprise applications may still rely on traditional SaaS, AI is democratizing high-quality software creation for a broader range of projects.
For SaaS providers, the message is clear: adapt or risk irrelevance. By integrating AI thoughtfully, embracing customization, rethinking pricing models, and enhancing security and support, traditional SaaS can evolve into a more integrated, AI-enhanced model that meets the diverse needs of modern software development.













